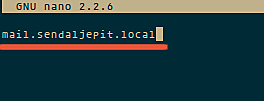
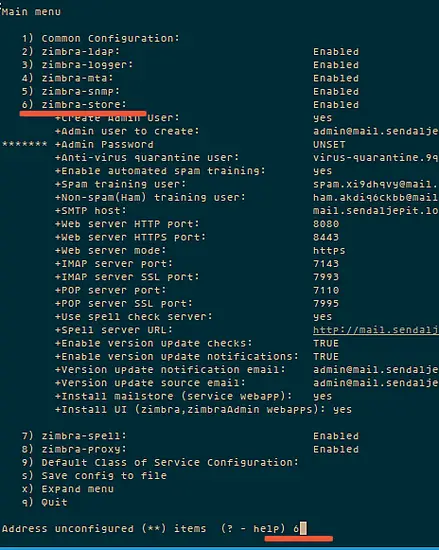
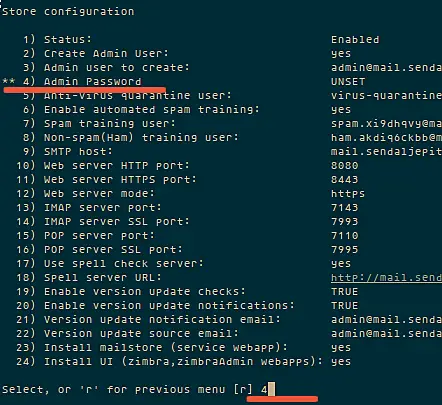
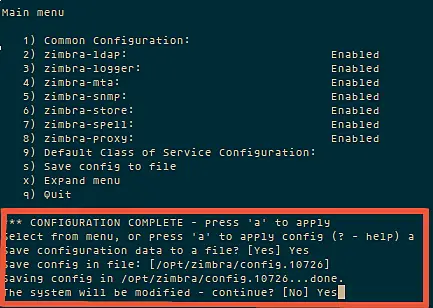
[root@localhost ~]#yum -y update
[root@localhost ~]#rpm –import http://repo.zabbix.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-ZABBIX
Installing repository configuration package
Install the repository configuration package. This package contains yum configuration files.
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/3.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-3.0-1.el7.noarch.rpmRetrieving http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/3.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-3.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm
Preparing… ################################# [100%]
Updating / installing…
1:zabbix-release-3.0-1.el7 ################################# [100%]
Installing Zabbix packages
Now Install Zabbix packages. Example for Zabbix server and web frontend with mysql database.
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-web-mysql mysql mariadb-server httpd phpHow to Install Zabbix Server 3.0 on linux environment
Creating initial database
Create zabbix database and user on MySQL. For instructions on doing that,
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start mariadb[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable mariadb
[root@localhost ~]# mysql_secure_installation
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we’ll need the current
password for the root user. If you’ve just installed MariaDB, and
you haven’t set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
… Success!
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
… Success!
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
… Success!
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
– Dropping test database…
… Success!
– Removing privileges on test database…
… Success!
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
… Success!
Cleaning up…
How to Install Zabbix Server 3.0 on linux environment
All done! If you’ve completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
[root@localhost ~]# mysql_secure_installation
MariaDB [(none)]>
MariaDB [(none)]> create database zabbix_db;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on zabbix_db.* to zabbix@localhost identified by ‘redhat’;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> exit
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/share/doc/zabbix-server-mysql-3.0.2/
[root@localhost zabbix-server-mysql-3.0.2]# gunzip create.sql.gz
[root@localhost zabbix-server-mysql-3.0.2]# mysql -u root -p zabbix_db < create.
sql
Starting Zabbix server process
Edit database configuration in zabbix_server.conf
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf DBHost=localhost DBName=zabbix DBUser=zabbix DBPassword=zabbix
Editing PHP configuration for Zabbix frontend
Apache configuration file for Zabbix frontend is located in /etc/httpd/conf.d/zabbix.conf. Some PHP settings are already configured.
php_value max_execution_time 300 php_value memory_limit 128M php_value post_max_size 16M php_value upload_max_filesize 2M php_value max_input_time 300 php_value always_populate_raw_post_data -1 # php_value date.timezone Asia/Dhaka After changing the configuration file restart the apache web server. Install Zabbix Server 3.0 on linux
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd Finally Start Zabbix server process by
[root@localhost ~]#service zabbix-server start Now you login your zabbix and install web content with Database.