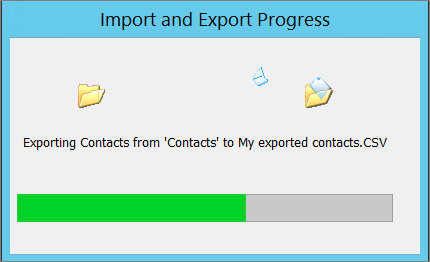
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security technology for
establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client—typically a
web server (website) and a browser; or a mail server and a mail client
(e.g., Outlook).
SSL allows sensitive information such as credit card numbers, social
security numbers, and login credentials to be transmitted securely.
Normally, data sent between browsers and web servers is sent in plain
text—leaving you vulnerable to eavesdropping. If an attacker is able to
intercept all data being sent between a browser and a web server they
can see and use that information.
More specifically, SSL is a security protocol. Protocols describe
how algorithms should be used; in this case, the SSL protocol
determines variables of the encryption for both the link and the
data being transmitted.
SSL secures millions of peoples’ data on the Internet every day,
especially during online transactions or when transmitting confidential
information. Internet users have come to associate their online security
with the lock icon that comes with an SSL-secured website or green
address bar that comes with an extended validation SSL-secured website.
SSL-secured websites also begin with https rather than http.
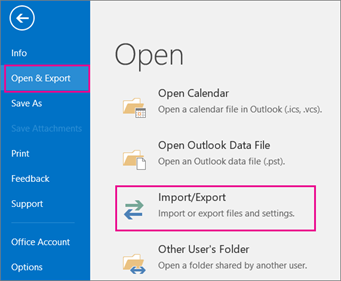
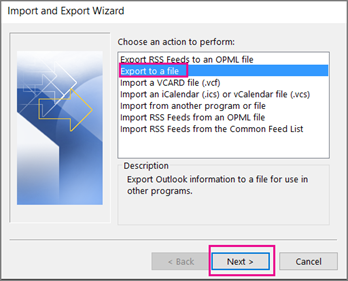
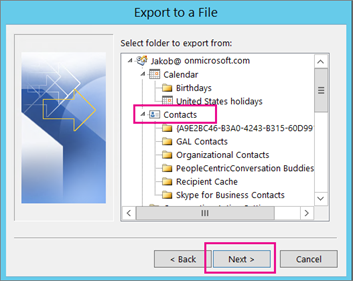
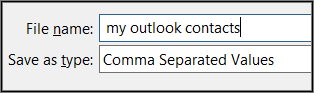
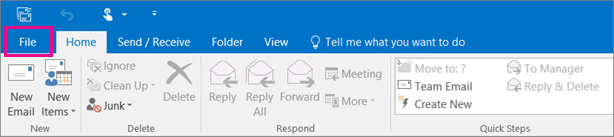 Now look at Outlook on your computer:
Now look at Outlook on your computer: